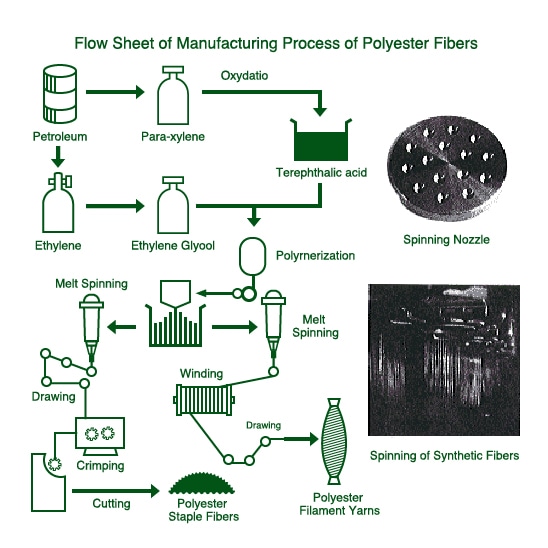
Polyester fibers are manufactured most abundantly among synthetic fibers. The amount of production is continuing to increase year by year. Polyester fibers have such features as extreme strength, resistance to crease, less moisture absorption, thermoplasticity, and resistance to acid and alkali.
In polyester fibers, both filament yarn and staple fibers are manufactured in nearly equal quantity. Filament yarns are woven or knitted as they are. In addition, they are knitted into jersey or woven into fabrics of textured yarn by combining with other types of filament yarns, twisting yarns and texturing in accordance with the aim of products. The filament yarns are processed into circular, triangular, oval, hollow and other cross-sections. Such processed fibers produce new fabrics of hand and luster not found in natural fibers without deteriorating the properties of polyester fibers. Furthermore, an extremely fine fibers of a tenth or hundredth part of silk fibers are manufactured and used for products of synthetic leather, synthetic suede and fabrics with high fabric count.
The staple fibers are friendly with other types of fibers. They are manufactured into fabrics, by blending with cotton, wool and linen fibers, making the use of each characteristic. The staple fibers are largely used for wadding as they are. By modifying their characteristics, anti-static fibers and flame-retardant fibers are also manufactured.